1. Tangent
The ratio for tangent is sin/cos. So the asymptotes are located when tangent is 0, this would only happen when cos is equal to 0. Since cos is the x-value the asymptotes are located where x=0. That would be at pi/2 and 3pi/2. If we recall from the unit circle all trig functions in the first quadrant are positive. Both sin and cos are pos. in the first quadrant so that means that when you divide one by the other, you end up with a positive value for tangent. For quad.2 we know that sin is positive and cosine is neg. This means we get a negative value for tangent.in the third quad. sin and cos are both negative so we get a positive value for tan. In quad 4sin is pos and cos is neg. A and get a neg. value for tangent. The graph for tangent is pos, neg, pos, neg. When we graph it within its period and based on the location of the asymptotes it will be uphill or downhill.
2. Cotangent
The trig ratio for cotangent is cos/sin. So the asymptotes are located where sin is equal to 0(y). The asymptotes would be located at 0 and 180 because y=0 there.To find out how the appearance for cotangent graphs we can use the trig ratio for cotangent looks, we can use the trig ratio for cot (cos/sin). Sin and cos are positive in the first quadrant, so when you divide one by the other, you end up with a positive value for cot. For quadrant 2 we get a negative value for cot. For the third quadrant we get a positive value for cot. In the fourth quadrant 4,we get a negative value. The graph for cotangent is pos, neg, pos, neg. When we graph it within its period of 0 and pi, the graph will begin close to the asymptote above the x-axis. When it enters second quad. it will be negative so we have to draw it downhill.
 |
| https://www.desmos.com/calculator/hjts26gwst |
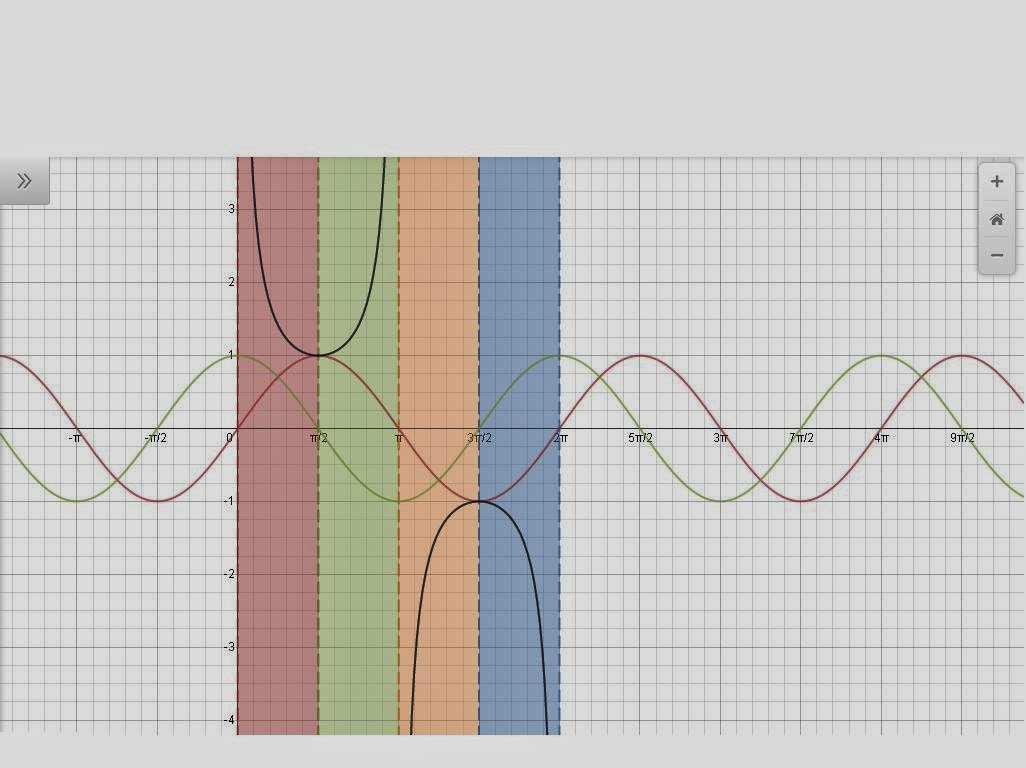
Secant is the reciprocal of cosine. It has a ratio of 1/cos. Since cosine is the denominator when it equals zero we will have asymptotes. Secant has asymptotes at pi/2 and 3pi/2(keep in mind that they go on forever to the left and right). These asymptotes are the only ones within the period. If secant is positive then the graph will go upward and if its negative the graph will go downward. Also if cosine is positive or negative secant will also.
 |
| https://www.desmos.com/calculator/hjts26gwst |
4.Cosecant?
Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine. It has a ratio of 1/sin. We get asymptotes when the denominator equals zero. Cosecant has asymptotes at 0 and pi (they keep going).If sine is positive so will the cosecant graph. Cosecant is also affected by that.
 |
| https://www.desmos.com/calculator/hjts26gwst |




